5. Image Processing
Corrections
Image processing is a process which makes an image interpretable for a specific use. There are many methods, but only the most common will be presented here.
Geometric Correction
The geometric correction of image data is an important prerequisite which must be performed prior to using images in geographic information systems (GIS) and other image processing programs. To process the data with other data or maps in a GIS, all of the data must have the same reference system. A geometrical correction, also called geo-referencing, is a procedure where the content of a map will be assigned a spatial coordinate system (for example, geographical latitude and longitude).
In geo-referencing, image points and pass points need to be searched, which then can be recognised in the coordinates. Pass points are usually determined with a GPS receiver on the terrain or with maps. Visual street crossings, bridges over water, etc. can be identified, and their coordinates will be noted. These points will then be coordinated with identical image points of the not yet geo-referenced satellite image. These correlations can ensure projections with the help of various additional procedures.
Radiometric Correction
System corrections are important, when technical defects and deficiencies of the sensor and data transfer systems lead to mistakes in the image data construction. Causes can be detector failure and/or power failure from detectors operating simultaneously.
In scanners such as Landsat TM and MSS with 6 respectively 15 scan rows which are used for the same spectral area, a failure of scan rows occurs. These errors always appear at the same intervals and create a characteristic striping (banding) in the image.
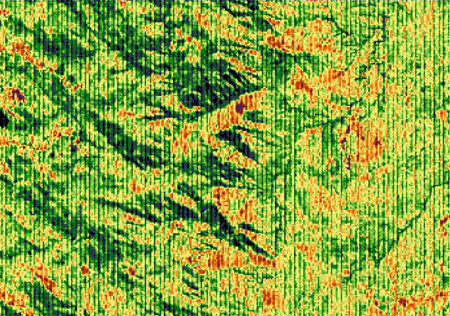
Source: Naumann 2008