1. Light and Life (3/8)
Answer: Sediment in the water, which scatters sunlight to the satellite sensor
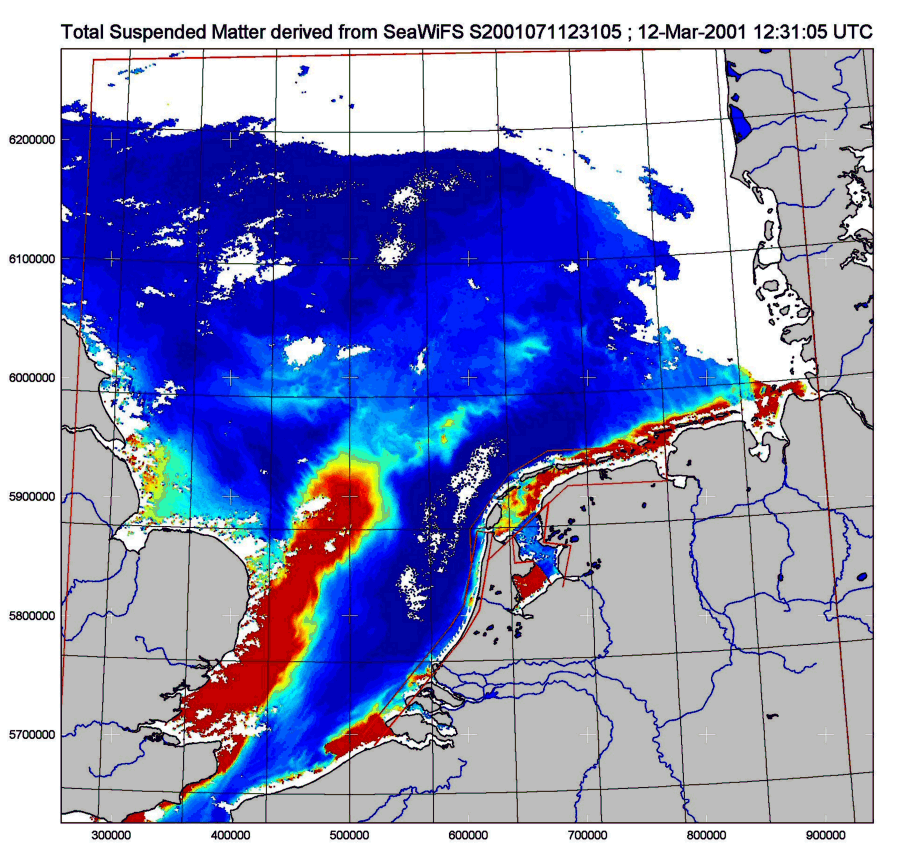
This map shows the shallow sea between Belgium, The Netherlands and England at 21st of March 2001. The sediment is measured in grams per cubic metre. In the world there are many rivers that bring sediment to the coastal zone. Sometimes this sediment can be seen as bright plumes that enter the more transparent waters in the ocean. A beautiful example is the coastal zone of Bangladesh that can be seen in the tutorial on A World of Images
Light for life: photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the conversion of light energy into chemical energy by living organisms. The raw materials used in this conversion are carbon dioxide and water; the energy source is sunlight; and the end-products are oxygen and the (energy rich) carbohydrates (starch and sugars) in plant cells. This is also presented in more detail in the SEOS tutorial on Remote Sensing in Agriculture.
Look at the overall reaction equation:
6 H2O + 6 CO2 ↔ C6H12O6 + 6O2
In case of photosynthesis the reaction balance dominates to the right, for respiration it is skewed to the left.
A plant needs the right amount of water and heat and energy (sunlight) to grow properly. In this experiment you are responsible for providing water and heat and light to a plant. Click once on the irrigation button (or the heat button) to start and a second time to stop.
