Chlorophyll and Photosynthesis
Chlorophyll molecules
Source: Wikimedia Commons.
Chlorophyll is a molecule (or more precisely, a family of very similar molecules) found mainly in plants, but also some bacteria and algae. Its purpose it to absorb light and use this energy to power the process of photosynthesis.
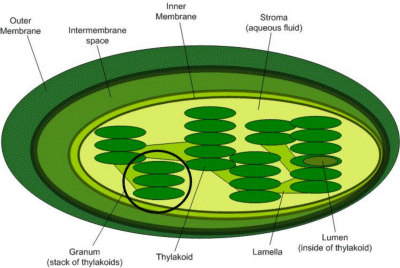
Cells of the organisms that have chlorophyll contain special constructions called chloroplasts. These are smaller versions of cells with their own membranes and internal organic components. A plant cell usually has many chloroplasts.
Within the chloroplasts, there are structures called granum, which are effectively stacks of "sacks", known as thylakoids. It is within those sacks that the chlorophyll molecules are found.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process through which carbon dioxide (CO2) and water are converted into glucose
(C2H12O6):
In order for this chemical reaction to function, energy is required in the form of photons (light). The power required for the process of photosynthesis is provided by the chlorophyll molecules. Chlorophyll absorbs energy in the visible region of the spectrum (particularly in the blue and red regions, and slightly less in the green region - which is why the leaves appear green to the human eye).
The energy absorbed by the chlorophyll molecules is used to break the C-O and H-O atomic bonds of CO2 and H2O and form the C-H and C-O bonds of glucose. Glucose functions as an energy storage molecule, containing energy in those C-H and C-O bonds. The glucose is then transferred to the entire plant through the vein system. Whenever the plant requires energy to initiate any chemical reaction, the atomic bonds of glucose break down, releasing the stored energy.
In addition to chlorophylls, other pigments such as the carotenoids and the anthocyanins absorb light at different wavelengths. Carotenoids absorb in the blue region (between 400 and 500 nm), while anthocyanins absorb primarily in the green region (between 500 and 600 nm).
Click here to download a short exercise on determining reflectance from known pigment concentration and determining pigment concentration from leaf reflectance.
Organisms that produce complex organic compounds from simple inorganic molecules are known as autotrophs. These organsims use light or oxidation of inorganic compounds as source of energy. On the other hand heterotrophs use autotrophs as a source of raw materials and energy.