3. 3D Applications
Drapes
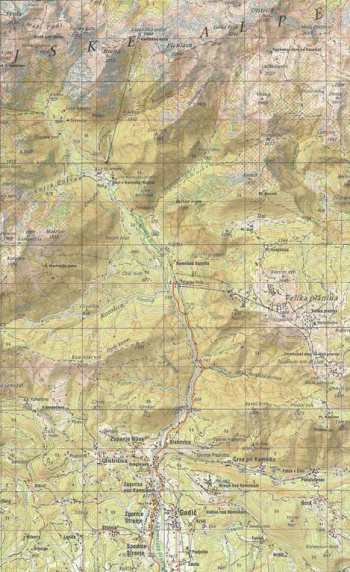
Do you still have problems with interpreting a topographical map?
For those who still have difficulty in interpreting elevation in satellite images, a new 3D presentation called drapes can be very helpful!
2D-images can be:
- aerial photographs
- satellite images
- scanned maps
- topographical maps
- geological maps
- orthophotos
- property maps
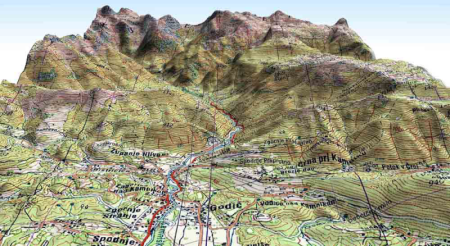
In the simplest terms, the 2D-image has been draped over the ground like spreading a blanket over an uneven surface. The ground is represented by the elevation model.

Source: Petrovič, Mašera, 2006
Viewing this 2D-image draped over a terrain surface helps to better understand the images and how they relate to the shape of the earth.
This mapping method is very useful especially in attaining information about remote and inaccessible areas. For example, in mountainous terrain, you can drape a satellite image over the elevation model to check access to proposed drilling sites.