Launched from Kourou in French Guiana on the night of 28 February 2002, Envisat is the largest Earth Observation spacecraft ever built.
Can you imagine ? It weighs 8.5 tonnes and is 10 m long, about the size of a double decker bus !

Artist's impression of Envisat. Source:
ESA.
ESA satellite Envisat flies in a sun-synchronous polar orbit of about 800-km altitude.
The repeat cycle of the reference orbit is 35 days, and for most sensors, being wide swath, it provides a complete coverage of the globe within one to three days.
Where is Envisat now ?
Envisat carries 10 sophisticated instruments to provide continuous observation and monitoring of the Earth's land, atmosphere, oceans and ice caps.
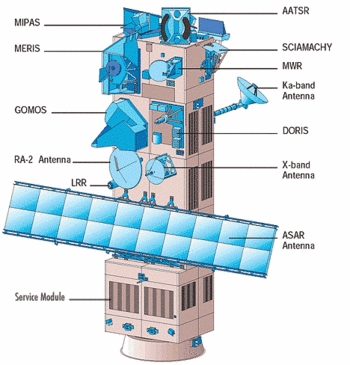
Envisat's instruments. Click on the instruments to get a detailled description.
Source:
Aviso.
ASAR
ASAR is an Advanced Synthetic Aperture Radar (ASAR). Operating at C-band, ASAR ensures continuity with the image mode
(SAR) and the wave mode of the ERS-1/2 AMI.
MERIS
MERIS is a programmable, medium-spectral resolution, imaging spectrometer operating in the solar
reflective spectral range. Fifteen spectral bands can be selected by ground command, each of which has a programmable width and a programmable
location in the 390 nm to 1040 nm spectral range.
AATSR
The prime scientific objective of the Advanced Along Track Scanning Radiometer (AATSR) is to establish
continuity of the ATSR-1 and ATSR-2 data sets of precise sea surface temperature (SST), thereby ensuring the production of a unique 10 year
near-continuous data set at the levels of accuracy required (0.3 K or better) for climate research and for the community of operational
as well as scientific users who have been developed through the ERS-1 and ERS-2 missions.
RA-2
Radar Altimeter 2 (RA-2) is an instrument for determining the two-way delay of the radar echo from
the Earth's surface to a very high precision: less than a nanosecond. It also measures the power and the shape of the reflected radar pulses.
MWR
The main objective of the microwave radiometer (MWR) is the measurement of the integrated atmospheric
water vapour column and cloud liquid water content, as correction terms for the radar altimeter signal. In addition, MWR measurement data
are useful for the determination of surface emissivity and soil moisture over land, for surface energy budget investigations to support
atmospheric studies, and for ice characterization.
GOMOS
GOMOS measures atmospheric constituents by spectral analysis of the spectral bands between 250 nm to
675 nm, 756 nm to 773 nm, and 926 nm to 952 nm. Additionally, two photometers operate in two spectral channels; between 470 nm to 520 nm and
650 nm to 700 nm, respectively.
MIPAS
The Michelson Interferometer for Passive Atmospheric Sounding (MIPAS) is a Fourier transform spectrometer
for the measurement of high-resolution gaseous emission spectra at the Earth's limb. It operates in the near to mid infrared where many
of the atmospheric trace-gases playing a major role in atmospheric chemistry have important emission features.
SCIAMACHY
SCIAMACHY is an imaging spectrometer whose primary mission objective is to perform global
measurements of trace gases in the troposphere and in the stratosphere.
DORIS
The Doppler Orbitography and Radio-positioning Integrated by Satellite instrument is a microwave
tracking system that can be utilized to determine the precise location of the ENVISAT satellite.
LRR
The LRR is a passive device which is used as a reflector by ground-based SLR stations using
high-power pulsed lasers. In the case of Envisat, tracking using the LRR is principally accomplished by the International Laser Ranging
Service (ILRS).


