Download Worksheet 'Satellites' for use in class. Find here the HTML version of the worksheet.
Objectives:
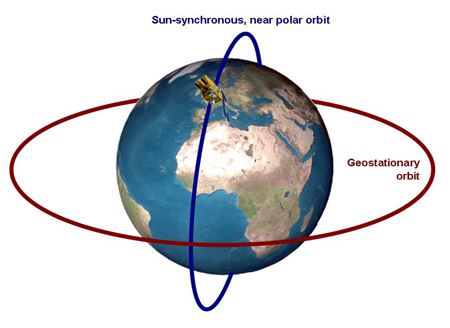
An earth observing satellite is an artificial flying object, orbiting around a planet (e.g. the earth) for scientific, commercial or military purposes. There are two different orbit: geostationary and near polar orbits.
Didactical comment:
- This worksheet asks the students to get familiar with the different satellites. The exercise teaches the students the differences between the two orbits, their applications as well as different types of satellites.
- First of all, it is important for the students to understand the distinction between possible applications of geostationary and near polar satellites, but also to establish a relationship between the satellites and everyday life.
Solution of Worksheet 'Satellites':
- Label both orbits in the image above.
- Explain why a satellite can fly around the earth without using energy.
- As the satellites are in orbit outside the atmosphere there is no air resistance and therefore, according to the law of inertia, the speed of the satellite is constant resulting in a stable orbit around the earth for many years.
- In a geostationary orbit at a distance of 36.000 km, the orbiting time is 24 hours corresponding to the earth's rotation time. At this altitude a satellite above the equator will appear stationary in relation to the earth.
- After leaving a stable orbit a satellite will reduce speed. A non-functioning satellite is the littering the orbits.
- The satellites in the 'red' orbit are used for several civilian services.
List some satellites and their uses and explain how they can affect your quality of life, both positively
and negatively.
- Example satellites in geostationary orbits are Meteosat, GOES, GMS, GOMS, KALPANA, and INSAT.
- Uses: Weather forecasting, telecommunication, broadcasting etc.
- Effects on our life and quality: (+) weather prediction in the news on TV and radio: telecommunication and broadcasting are part of in everyday life.
- (-) old and broken satellites or parts are littering the orbits and threaten functioning satellites.
- Why are the satellites shown in the 'blue' orbit important for earth observation?
- They give an overview of (large) areas for the last 30 years.
- They are continuously observing the earth and sending data to the ground stations.
- They help to monitor the environment and changes on the earth's surface, covering everything from urban planning to vegetation monitoring etc. depending on the spatial resolution.
- These satellites have multiple uses, e.g. disaster monitoring, mapping, digital elevation model building, agricultural mapping, traffic control etc.
- Changes can also be compared easily because the satellites record an area always at the same local time (they are sun-synchronous).
- Assign the following satellites to their correct orbits by writing the satellite names next to the correct orbit: Landsat, KALPANA, IRS, Meteosat, INSAT, Radarsat, SPOT, GMS, QuickBird, GOES, ERS, GOMS, Envisat, Ikonos, NOAA.
| Sun-synchronous, near polar orbit | Geostationary orbit |
| Landsat | Meteosat |
| IRS | GOES |
| Radarsat | GMS |
| SPOT | GOMS |
| QuickBird | KALPANA |
| ERS | INSAT |
| Envisat | |
| Ikonos | |
| NOAA |
Download Worksheet 'Satellites' for use in class. Find here the HTML version of the worksheet.