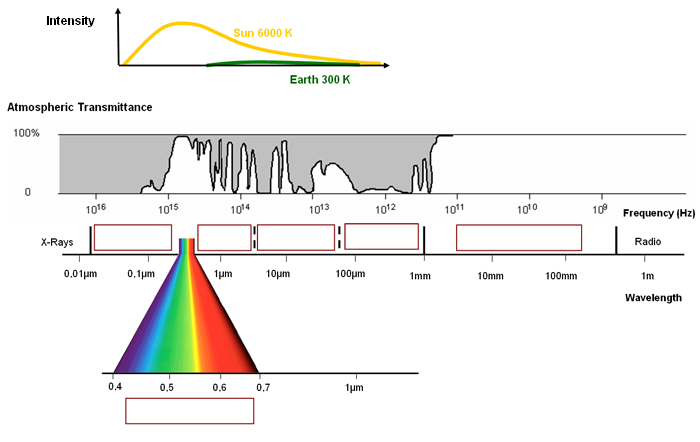
The electromagnetic spectrum
| Measured: | Reflected solar radiation | Emitted thermal radiation | ||||
| Atmospheric influence: | In the blue & green range | Marginal | ||||
| Applications: | Mapping of biomass and vitality/ damage of vegetation | Radar detection, meteorological applications, land shifting |
Tasks:
Use the following words to describe the different spectral areas of the electromagnetic spectrum and to complete the accompanying table:
Near-IR - Detection of surface temperatures, soil moisture - Visible - Microwave - Reflected solar radiation -
Mid-IR - Very high - Marginal - Ultraviolet - Detection of vegetation and soil moisture, geological applications, ocean currents -
Visible Light - Marginal - Oil films on water, ozone concentration - Few - Microwave - Thermal IR -
Emitted thermal radiation- Near-IR - Reflected solar radiation - Detection of vegetation, water bodies and soils for land cover and land use mapping -
Ultraviolet - Thermal IR - Emitted & reflected radiation - Mid-IR.
