1. Physical Basics
Interaction of radiation with the earth surface
Electromagnetic radiation incident on the surface of a body is partly reflected, partly absorbed or transmitted d epending on radiation wavelength, material and surface conditions of the body. The distinctness of different bodies allow us to distinguish between them on a satellite image.
Besides the angle of incidence, it is primarily the surface roughness which determines the way how an object reflects radiation. One can distinguish different types of reflectance:
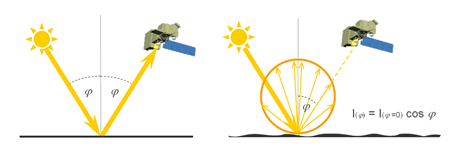
- Specular: flat surfaces reflect like a mirror (where the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence)
- Diffuse (or Lambertian): rough surfaces reflect uniformly in all directions
Most earth surfaces are neither perfectly specular nor diffuse and lie somewhere between the two extremes.
The type of reflectance depends on the surface's roughness and the wavelength of incident radiation reaching the surface. Wavelengths which are smaller than the surface height variations lead to a diffuse reflectance.
Diffuse reflectances of earth surfaces are very important in remote sensing because only diffuse reflections contain spectral information on the "colour" of the reflecting surface. Specular reflections do not (Lillesand, Kiefer 2004).
Supplement: Applications of different bands or wavelength ranges