GIWA is a water programme led by the United Nations Environment Programme, UNEP. The aim of the programme is to assess the ecological status and the causes of environmental problems in 66 water areas in the world.
The assessment focuses on the environmental conditions and problems in transboundary (cross-national) waters, comprising marine, coastal and freshwater areas, and surface waters as well as ground waters.
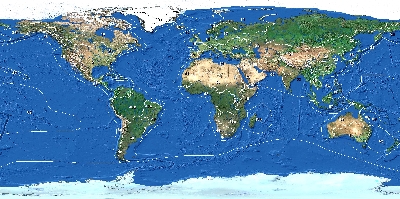
Global map of the 66 water regions that are covered by GIWA.
Source: GIWA
The overall objective of GIWA is to develop a comprehensive strategic assessment that may be used to identify priorities for remedial and mitigatory actions in international waters, designed to achieve significant environmental benefits at national, regional and global levels.
GIWA is designed not merely to analyse the current problems and their societal root causes, but to develop scenarios of the future condition of the world's water resources and analyse policy options.
Ultimately, the aim is to provide sound scientific advice to decision-makers and managers concerned with water resources and dealing with environmental problems and threats to transboundary water bodies.
GIWA is focusing on five major problem areas, including 23 specific environmental and socio-economic problems.
Socio-economic impacts of pollution according to GIWA methodology
- Increased risk to human health
- Increased cost of human health protection
- Loss of water supplies
- Increased clean up costs
- Loss of tourism or recreational values
- Loss in fisheries
- Loss of property value
- Potential for international conflicts
- Damage to equipment
- Endangerment of species
- Costs of litigation
Environmental impacts of pollution according to GIWA methodology
1. Microbiological
↓↑
- Aquatic organisms infections and disease
2. Eutrophication
↓↑
- Redox changes (extreme anoxia)
- Increased algal blooms
- Changes in algal community structure
- Changes in macrophyte community structure
- Loss of habitat (e.g. coral reefs)
3. Chemical
↓↑
- Reproductive disfunction in aquatic organisms
- Behavioural disfunction in aquatic organisms
- Modified community structure
- Increased mortality of aquatic organisms
4. Suspended solids
↓↑
- Habitat modification
- Changes in biological community composition
- Changes in the growth/survival/reproduction of species
- Enhanced erosion of coastal and river channels
- Increased sediment deposition
- Destruction of benthic communities
- Changes in sediment redox conditions
5. Solid waste
↓↑
- Habitat loss
- Hydraulic modification
- Suffocation of marine organisms
- Beach and sediment compositional changes
6. Thermal
↓↑
- Population changes
- Barriers to migration
- Displacement of organisms
- Changes to physical environment
7. Radionuclide (from anthropogenic sources)
↓↑
- Proximal and stochastic risks to animal life
8. Spills
↓↑
- Increased avian mortality
- Increased mortality of aquatic life
- Habitat damage
- Long term contamination of sediments and beaches with associated ecological changes

Front cover of the GIWA final report.
Source: GIWA
|

Front cover of the GIWA Baltic Sea report.
Source: GIWA
|
Immediate causes of marine pollution as identified in GIWA
1. Microbiological pollution
↓↑
- Discharge of effluents
- Discharge of animal wastes
- Discharge of solids
- Atmospheric deposition
- Remobilisation and leaching
- Runoff and storm-water
- Altered circulation (flushing of rivers, lakes, coastal systems)
2. Eutrophication
↓↑
- Enhanced discharge of effluents
- Enhanced discharge of solids
- Runoff and storm waters
- Increased recycling/mobilisation
- Trapping of nutrients (e.g. in river impoundments)
- Inputs from atmospheric deposition
3. Chemical pollution
↓↑
- Discharge of effluents
- Discharge of solids
- Runoff and storm waters
- Leachates from landfills
- Chemical releases (e.g. from aquaculture)
- Release from mining
- Weed and pest control
- Disease vector control
- Emmissions from fossil fuel combustion (electrical and vehicle)
- Increased combustion of natural vegetation
4. Suspended solids
↓↑
- Soil and sediment erosion, remobilisation and leaching
- River and stream alteration
- Dredging and dredge spoil activities
- Mining releases
- Discharge of effluents
- Discharge of drilling mud and particulate additives
- Runoff and storm waters
5. Solid wastes
↓↑
- Releases from ships and offshore platforms
- Sewage related debris
- Discards of beach users
- Municipal/industrial solid wastes
- Releases from landfills
- Tar balls
- Releases from land development
6. Thermal pollution
↓↑
- Cooling water discharge
- Removal of riparian belts (includig trees) exposing the water to direct sunlight
- Elevated suspended solids due to soil erosion
7. Radionuclides
↓↑
- Incidents at sea
- Spills from treatment facilities
- Discharges/emissions from nuclear power plants
- Discharges/emissions from nuclear fuel reprocessing plants
- Accidents involving nuclear-powered vessels
- Fallout from nuclear weapons tests
8. Accidental spills
↓↑
- Shipwreck or collision
- Operational accidents
- Breaching of waste containment dams/ponds
- Force majeure
More information about the GIWA methodology can be found on the GIWA homepage (external link).



